|
| Links to related material and teachers' resources | |
| Pitch, loudness and timbre
Frequency and pitch. Amplitude and loudness. Timbre examples, with envelope and spectrum. |
 |
|
Transverse vs longitudinal waves. y(x') in a longitudinal wave. Density variations. A travelling longitudinal wave. Variations in pressure give rise to accelerations. |
 |
|
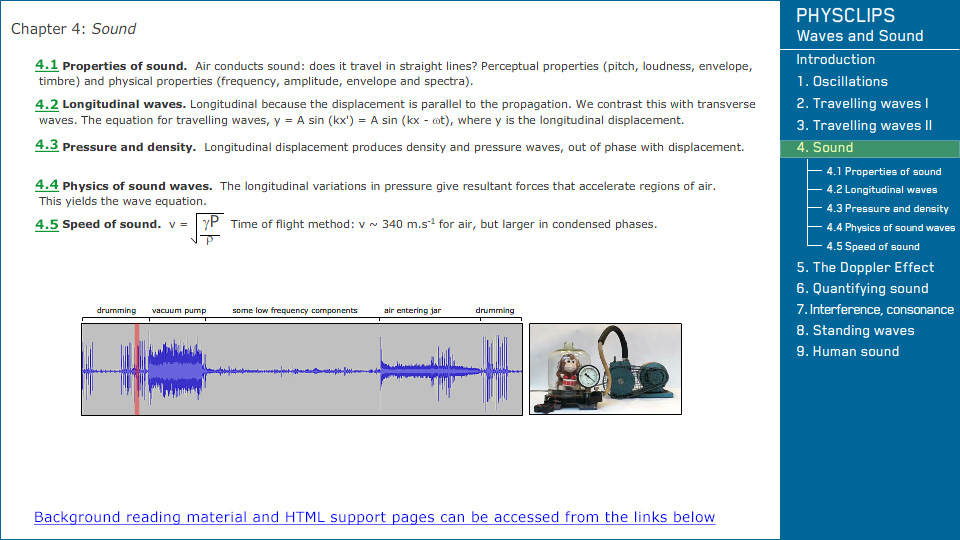
Sound transmission through air. Bell jar experiment. If sound diffracts, why doesn't light? |
 |
|
Time-of-flight measurements of the speed of sound. Clap-echo measurement. Clap-board (image vs sound) measurement. Experiments using two microphones and a long cable. |
 |
| Adiabatic expansion and compression The relationship between pressure, volume and temperature for a rapid (adiabatic) change in volume of a gas. |
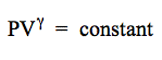 |
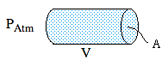
Displacement, compression and pressure. Newton's second law and acceleration. The wave equation for sound. Speed of sound. Acoustic impedance.
|
|
Acoustic compliance, inertance and impedance |
 |
Acoustic impedance, intensity and power |
 |
What is a decibel? |
 |
| The Mexican Wave The mexican wave (or stadium wave) is an example of a transverse, polarised, travelling wave. An interesting idea for teachers: the wave speed can be faster than the particle speed. |
 |
| Downloads (thumbnails at 50% of size of animation) |
|
||||