|
| Links to related material and teachers' resources |
Background material for circular motion |
Vectors Vectors, vector components, unit vectors, two and three dimensions, vector addition and subtraction, relative motion and moving coordinates, the scalar product of vectors (the dot product), the vector product (the cross product) |
A simple introduction to calculus: Differentials
and integrals
|
Download
all animations in this chapter (
mp4 videos
/
original flash files )
Circular motion |
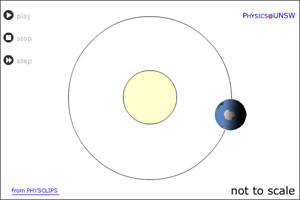 |
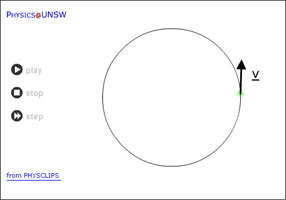 |
|
| Download
(mp4 video) Download (original flash file) |
Download
(mp4 video) Download (original flash file) |
|
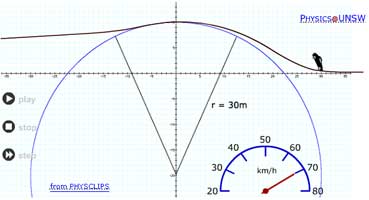 |
|
| Download
(mp4 video) Download (original flash file) |
|
||||